-
16 Jul 2024
GS Paper 1
Indian Society
Day 8: Despite numerous government initiatives aimed at eradicating poverty in India, poverty continues to persist. Critically examine. (250 words)
Approach
- Give a brief introduction to the extent of poverty in India.
- Mention key government initiatives aimed at eradicating poverty in India
- Highlight the reasons for persistent poverty in India.
- Suggest measures to eradicate poverty.
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
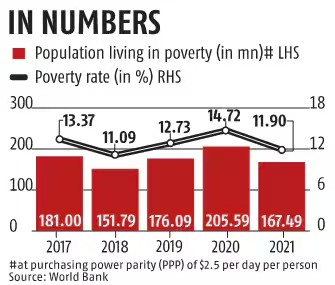
Poverty is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various dimensions of deprivation, primarily characterized by a lack of financial resources and access to essential services.According to the NITI Aayog, India has registered a significant decline in multidimensional poverty in India from 29.17% in 2013-14 to 11.28% in 2022-23 i.e. a reduction of 17.89 percentage points.Despite significant economic growth and extensive government efforts to alleviate poverty in India , a considerable proportion of the population still experiences various forms of poverty.
Body
Government Initiatives to Eradicate Poverty
- Economic Reforms and Growth: Economic liberalization policies initiated in the 1990s aimed to stimulate growth and create job opportunities.
- Programs such as Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), have provided guaranteed employment and wages to rural households.
- Social Welfare Programs: Various schemes like the Public Distribution System (PDS), Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY), and Swachh Bharat Mission have been designed to provide essential services and improve living conditions.
- Education and Skill Development: Initiatives like the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) and the National Skill Development Mission focus on enhancing educational opportunities and vocational training, aiming to improve employability and income levels among the poor.
- Healthcare Programs: The National Health Mission (NHM) and Ayushman Bharat scheme are intended to improve healthcare access and affordability, thus addressing one of the critical barriers to escaping poverty.
Reasons for Persistent Poverty
- Inequality and Exclusion: Economic growth has not been uniformly distributed, leading to significant income inequality.
- Marginalized groups, including Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and women, often face systemic exclusion and limited access to resources, exacerbating poverty.
- Implementation Gaps: Many programs suffer from poor implementation, including issues such as corruption, inefficiency, and lack of accountability.
- Leakages in subsidy distribution and inadequate monitoring mechanisms undermine the effectiveness of poverty alleviation efforts.
- Structural Issues: Structural problems such as inadequate infrastructure, limited access to markets, and poor connectivity in rural areas hinder economic development and perpetuate poverty.
- The rural-urban divide and regional disparities also contribute to uneven progress.
- Education and Skills Mismatch: While educational programs have expanded, there is often a mismatch between the skills taught and the demands of the labor market.
- This results in high unemployment and underemployment among the poor, who struggle to find suitable employment.
- Health and Social Challenges: Poor health conditions and lack of access to quality healthcare impede individuals’ ability to work and improve their socio-economic status.
- Additionally, social challenges such as domestic violence and gender discrimination further entrench poverty.
- Funding and Resource Constraints: Insufficient funding and resources for poverty alleviation programs often limit their reach and impact.
- Budgetary constraints and competing priorities can lead to underfunded programs and insufficient support for the most vulnerable populations.
- Administrative Inefficiencies: Bureaucratic inefficiencies and delays in program execution can reduce the effectiveness of poverty alleviation efforts.
- Streamlining administrative processes and improving coordination among various stakeholders is crucial for better outcomes.
Conclusion
According to Amartya Sen,a renowned economist and Nobel laureate, poverty should be seen not just as a lack of income but as a deprivation of basic capabilities. Ensuring that people have the freedom to achieve various functionings, such as being healthy, educated, and socially active, is crucial for true poverty eradication. A more holistic approach, integrating economic, social, and institutional reforms, is essential to tackle the root causes of poverty effectively.




